使用基于化学探针的免疫测定直接测量KDM1A目标参与
Summary
在这里,我们提出一个协议,以测量KDM1A靶向在使用KDM1A抑制剂处理的人或动物细胞、组织或血液样本中的参与度。该协议采用自由KDM1A酶的化学探针标记,并使用基于化学探针的免疫测定直接定量目标职业,可用于临床前和临床研究。
Abstract
对靶向参与的评估,即药物与其设计的蛋白质相互作用,是解释药物开发或基础研究项目中任何化合物的生物活性的基本要求。在表观遗传学中,目标参与度通常通过分析代理标记而不是测量化合物与目标的结合来评估。已分析的下游生物读出包括组蛋白标记调制或基因表达变化。KDM1A是一种以源脱甲基酶,从单甲基和二甲基化H3K4中去除甲基组,这是一种与基因表达沉默相关的修饰。代理标记的调制取决于被调查细胞的细胞类型和功能,这使得解释和交叉案例比较相当困难。为了规避这些问题,提出了一个通用的协议,以评估直接KDM1A目标参与的剂量效应和动态。所述测定利用KDM1A化学探针捕获和量化无抑制酶,可广泛应用于细胞或组织样本,无需基因改造,具有极好的检测窗口,可用于基础研究临床样本分析。
Introduction
莱辛特异性脱甲基酶1(KDM1A)1是一种参与控制基因转录的脱甲基酶。这种蛋白质已成为肿瘤学的候选药理靶点2;包括急性骨髓性白血病3(AML),骨髓增生综合征(MDS)4,骨髓纤维化(MF)5,6,小细胞肺癌(SCLC)7;在病变细胞病(SCD)8,9,和在中枢神经系统疾病,包括阿尔茨海默氏病(AD),多发性硬化症(MS);并在侵略10。
临床开发中的大多数KDM1A抑制化合物是环丙胺衍生物,通过共价结合其片苷二核苷酸(FAD)联因子11来抑制蛋白质。KDM1A的抑制诱导基因表达变化,但这些变化在组织、细胞类型或疾病病例之间变化很大。抑制KDM1A也改变组蛋白标记12,但这些变化一般在基因组的特定部位本地产生,并再次是高度组织和细胞特异性。
该协议旨在直接测量KDM1A目标在生物样品中的参与度,并针对环丙胺衍生抑制剂的使用进行了优化。该测定基于ELISA技术,并并行分析从生物样品中提取的天然蛋白质提取物中的KDM1A(非约束抑制剂)。作为第一步,生物样品在存在生物异化KDM1A选择性化学探针OG-88113,14,来自选择性KDM1A抑制剂ORY-1001(iadademstat),一种临床KDM1A的强效抑制剂的存在下进行。肿瘤病的治疗发展。化学探针具有 IC50,用于 KDM1A 的 120 nM,并包括与生物素化聚乙烯乙二醇 (PEG) 尾部相关的 FAD 结合功能。化学探针专门绑定到游免费的KDM1A,但不与样品中的抑制剂结合的KDM1A结合。在化学探针结合后,在具有链球菌素涂层表面的微子板上捕获含有复合物的KDM1A,以确定游脱KDM1A,或在涂有单克隆抗KDM1A捕获抗体的板上捕获,以确定总KDM1A。洗涤后,两个板均用抗KDM1A检测抗体孵育,再次洗涤,并用二级HRP结合的驴抗兔IgG抗体孵育,使用发光基板进行检测,并通过测量相对光照仪 (RLU) 中的光度计 (图 1)。
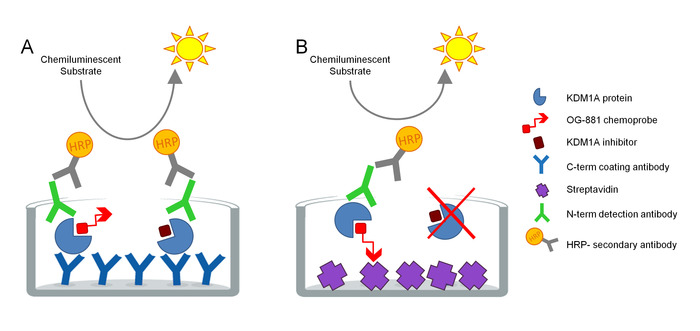
图 1.ELISA酶与化学探针免疫吸收测定的架构为KDM1A靶点:A)使用三明治ELISA和B确定总KDM1A(使用化学探针ELISA)的游出KDM1A。请点击此处查看此图的较大版本。
两个 ELISA 板中都包含一条标准曲线,用于验证每个测定的线性度。然后,将确定每个样品中的KDM1A目标参与度作为预剂量或车辆处理样品的相对值计算。
Protocol
Representative Results
Discussion
此处介绍的协议是使用基于新型 KDM1A 化学探针捕获的 ELISA 直接测量 KDM1A 目标参与度的。该方法已对培养的人类细胞系和来自人类、大鼠和小鼠和巨蜥(包括PBMC、肺、大脑、皮肤、肿瘤)的体外样本进行了验证,但可随时应用于KDM1A抗体靶向表位和催化的其他物种中心是保存的。由于OG-881是一种基于活性的化学探针,样品质量很重要,因此,特别是在协议的初始步骤中,应进行适当的操作和保护,以确保KDM1A…
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Acknowledgements
这项研究由奥里松基因组学资助。S.A.,霍夫曼-拉罗氏,部分支持CIIP-20152001和RETOS合作项目RTC-2015-3332-1。
Materials
| 0,05% Trypsin-EDTA (1X) | Thermo Scientific | #25300-062 | |
| 10 X Protease Inhibitor Tablets | Roche | #11836153001 | |
| 96 deep well storage block | VWR | #734-1679 | |
| 96 well ELISA plates | Nunc | #436110 | |
| Adhesive black Film | Perkin Elmer | #6050173 | |
| Adhesive transparent Film | VWR | #60941-062 | |
| Biotinylated KDM1A probe OG-881 | Oryzon Genomics S.A. | NA | |
| Bovine Serum Albumin | Sigma | # 3117057001 | |
| Bovine Serum Albumin Standard | Thermo Scientific | #23208) | |
| Bradford Protein Assay | BioRad | #500-0001 | |
| Cell lysis buffer 10X | Cell Signaling | #9803 | |
| Centrifuge for 96- well plates | Hettich | Rotina 420R | |
| Flask | Thermo Scientific | #156499 | |
| Full length, enzymatically active human Recombinant LSD1 / KDM1A | Active Motif | #31426 | |
| Graphpad Prism 5 Project | GraphPad Software | NA | |
| Luminol-Enhacer and Peroxide Solution (Chemiluminescent Substrate) | Thermo Scientific | #37074 | |
| Micro Centrifuge | Eppendorf | 5415 R | |
| Microplate reader Infinite 200-Tecan | Tecan | Infinite 200 | |
| Mouse monoclonal capture antibody Anti-KDM1A (N-terminal epitope) | Abcam | #ab53269 | |
| Needle G18 gauge blunt | BD | #303129 | |
| ORY-1001 (iadademstat) | Oryzon Genomics S.A. | NA | |
| PBMC separation tubes 10 ml | Greiner bio-one | #163288 | |
| PBMC separation tubes 50 ml | Greiner bio-one | #227288 | |
| PBS 1x | Sigma | #D8537 | |
| Plate shaker | Heidolph Instruments | Rotamax 120 | |
| Polysorbate 20 | Sigma | #P7949 | |
| Rabbit monoclonal detection antibody Anti-KDM1A (C-terminal epitope) | Cell Signaling | #672184BF-100 | |
| Secondary antibody Peroxidase-conjugated Donkey Anti-rabbit IgG | Thermo Scientific | #31458 | |
| Spectrophotometer cuvette 1.5 | Deltalab | #302100 | |
| Spectrophotometer for cuvette | GE Healthcare | GeneQuant 1300 | |
| Streptavidin | Promega | #Z704A | |
| Syringe | BD | #303172 | |
| Type 1 ultrapure water | Millipore | Milli-Q Advantage A10 | |
| Ultrasonic cleaner | VWR | USC200T |
References
- Shi, Y. Histone demethylation mediated by the nuclear amine oxidase homolog LSD1. Cell. 119 (7), 941-953 (2004).
- Maiques-Diaz, A., Somervaille, T. C. LSD1: biologic roles and therapeutic targeting. Epigenomics. 8 (8), 1103-1116 (2016).
- Maes, T. ORY-1001, a Potent and Selective Covalent KDM1A Inhibitor, for the Treatment of Acute Leukemia. Cancer Cell. 33 (3), 495-511 (2018).
- Sugino, N. A novel LSD1 inhibitor NCD38 ameliorates MDS-related leukemia with complex karyotype by attenuating leukemia programs via activating super-enhancers. Leukemia. 31 (11), 2303-2314 (2017).
- Kleppe, M., Shank, K., Efthymia, P., Riehnhoff, H., Levine, R. L. Lysine-Specific Histone Demethylase, LSD1, (KDM1A) As a Novel Therapeutic Target in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Blood. 126, 601 (2015).
- Jutzi, J. S., et al. LSD1 Inhibition Prolongs Survival in Mouse Models of MPN by Selectively Targeting the Disease Clone. HemaSphere. 2 (3), 54 (2018).
- Mohammad, H. P. DNA Hypomethylation Signature Predicts Antitumor Activity of LSD1 Inhibitors in SCLC. Cancer Cell. 28 (1), 57-69 (2015).
- Rivers, A., et al. RN-1, a potent and selective lysine-specific demethylase 1 inhibitor, increases γ-globin expression, F reticulocytes, and F cells in a sickle cell disease mouse model. Experimental Hematology. 43 (7), 546-553 (2015).
- Rivers, A. Oral administration of the LSD1 inhibitor ORY-3001 increases fetal hemoglobin in sickle cell mice and baboons. Experimental Hematology. 67, 60-64 (2018).
- Buesa, C., et al. The dual LSD1/MAO-B inhibitor ORY-2001 prevents the development of the memory deficit in samp8 mice through induction of neuronal plasticity and reduction of neuroinflammation. Alzheimer’s & Dementia. 11 (7), P905 (2015).
- Schmidt, D. M., McCafferty, D. G. Trans-2-Phenylcyclopropylamine is a mechanism-based inactivator of the histone demethylase LSD1. Biochemistry. 46 (14), 4408-4416 (2007).
- Forneris, F., Binda, C., Vanoni, M. A., Battaglioli, E., Mattevi, A. Human histone demethylase LSD1 reads the histone code. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 280 (50), 41360-41365 (2005).
- Gonz#225;lez, E. C., Maes, T., Crusat, C. M., Mu#241;oz, A. O. Oryzon Genomics, Methods to determine kdm1a target engagement and chemoprobes useful therefor. , (2016).
- Mascaró, C., Ortega, A., Carceller, E., Rruiz Rodriguez, R., Cicero, F., Lunardi, S., Yu, L., Hilbert, M., Maes, T. Chemoprobe-based assays of histone lysine demethylase 1A target occupation enable in vivo pharmacokinetics and -dynamics studies of KDM1A inhibitors. Journal of Biological Chemistry. , (2019).
- Rodriguez-Suarez, R. Development of Homogeneous Nonradioactive Methyltransferase and Demethylase Assays Targeting Histone H3 Lysine 4. Journal of Biomolecular Screening. 17 (1), 49-58 (2011).
- Lynch, J. T., Cockerill, M. J., Hitchin, J. R., Wiseman, D. H., Somervaille, T. C. CD86 expression as a surrogate cellular biomarker for pharmacological inhibition of the histone demethylase lysine-specific demethylase 1. Analytical Biochemistry. 442 (1), 104-106 (2013).
- Schulz-Fincke, J. Structure-activity studies on N-Substituted tranylcypromine derivatives lead to selective inhibitors of lysine specific demethylase 1 (LSD1) and potent inducers of leukemic cell differentiation. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 144, 52-67 (2018).
- Ishii, T., et al. CETSA quantitatively verifies in vivo target engagement of novel RIPK1 inhibitors in various biospecimens. Scientific Report. 7, 13000 (2017).
- Maes, T. ORY-2001: An Epigenetic drug for the treatment of cognition defects in Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Alzheimer’s & Dementia. 12 (7), P1192 (2017).

